Why Blood Sugar Levels Rise Overnight
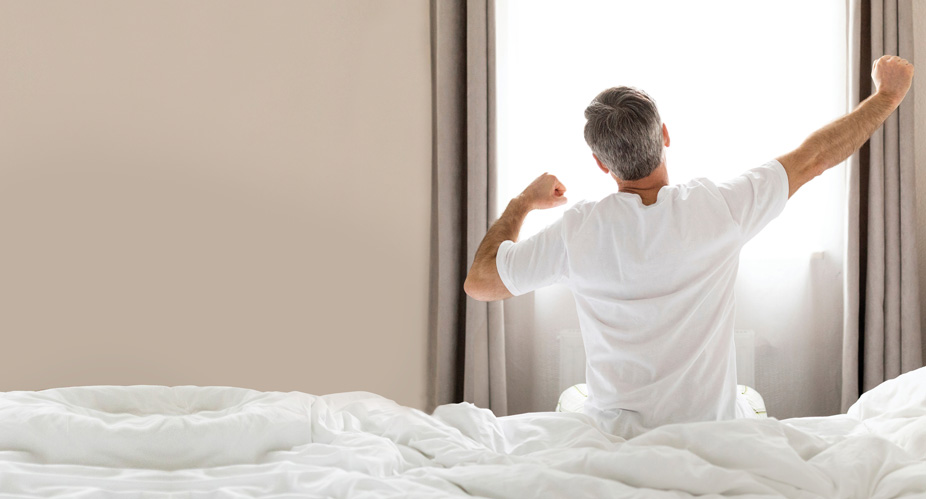
When you go to bed, your blood sugar reading is 6 mmol/L, but when you wake up in the morning, it has shot up to 15 mmol/L. Why does this happen?
To better understand this phenomenon, it is important to know the role of insulin in our bodies. So, what is insulin and what does it do? Insulin is a hormone that lowers blood sugar by moving glucose from your blood into cells all over your body.
During the day, the carbohydrates we eat are digested into glucose and absorbed into the bloodstream. Some of this glucose goes to the liver, where it is stored for later use.
At night, while we are asleep, the liver releases glucose into the bloodstream. The liver acts as our glucose warehouse and keeps us supplied until we eat breakfast. Insulin works as the messenger to tell the liver how much glucose should be released, so blood sugar levels remain constant.